摘要: Pandas数据加载存储相关的学习笔记,记录了《利用python进行数据分析》学习过程和笔记。
本部分为pandas的输入输出对象。
1 读写文本格式的数据
先上表,其中read_csv和read_table最常用。
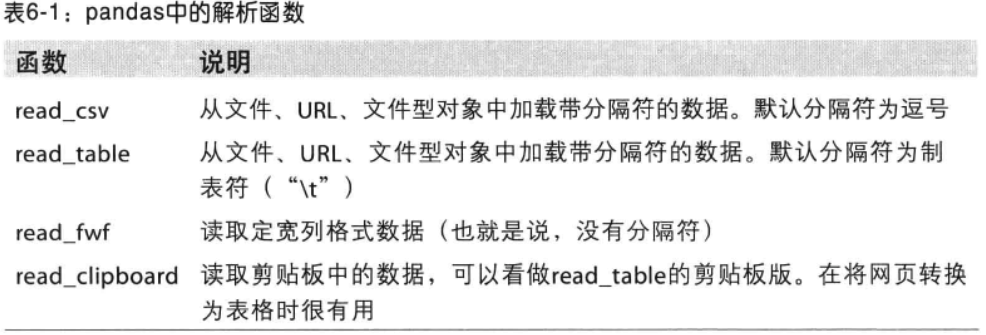
这些函数的选项可以划分几类:
- 索引:
- 类型推断和数据转换:
- 日期解析:
- 迭代:
- 不规整数据问题:
类型推断(type inference):不需要指定数据类型,可以自动识别。
In [286]: df = pd.read_csv('../source/ch06/ex1.csv')
In [287]: df
Out[287]:
a b c d message
0 1 2 3 4 hello
1 5 6 7 8 world
2 9 10 11 12 foo
In [289]: pd.read_table('../source/ch06/ex1.csv',sep=',')
Out[289]:
a b c d message
0 1 2 3 4 hello
1 5 6 7 8 world
2 9 10 11 12 foo
In [290]: cat ../source/ch06/ex2.csv
1,2,3,4,hello
5,6,7,8,world
9,10,11,12,foo
In [291]: pd.read_csv('../source/ch06/ex2.csv',names=['a','b','c','d','message'])
Out[291]:
a b c d message
0 1 2 3 4 hello
1 5 6 7 8 world
2 9 10 11 12 foo
In [292]: names=['a','b','c','d','message']
In [293]: pd.read_csv('../source/ch06/ex2.csv',names=names, index_col='message')
Out[293]:
a b c d
message
hello 1 2 3 4
world 5 6 7 8
foo 9 10 11 12
read_csv时可以使用skiprows跳过文件的某些行。
In [294]: !cat ../source/ch06/ex4.csv
# hey!
a,b,c,d,message
# just wanted to make things more difficult for you
# who reads CSV files with computers, anyway?
1,2,3,4,hello
5,6,7,8,world
9,10,11,12,foo
In [295]: pd.read_csv('../source/ch06/ex4.csv',skiprows=[0,2,3])
Out[295]:
a b c d message
0 1 2 3 4 hello
1 5 6 7 8 world
2 9 10 11 12 foo
In [296]: !cat ../source/ch06/ex5.csv
something,a,b,c,d,message
one,1,2,3,4,NA
two,5,6,,8,world
three,9,10,11,12,foo
In [297]: pd.read_csv('../source/ch06/ex5.csv')
Out[297]:
something a b c d message
0 one 1 2 3.0 4 NaN
1 two 5 6 NaN 8 world
2 three 9 10 11.0 12 foo
In [298]: result = pd.read_csv('../source/ch06/ex5.csv')
In [299]: result.isnull()
Out[299]:
something a b c d message
0 False False False False False True
1 False False False True False False
2 False False False False False False
read_csv/read_table选项:


1.1 逐块读取文本文件
当文件太大时候,我们只想读取其中一部分。
In [303]: result = pd.read_csv('../source/ch06/ex6.csv',nrows=5)
In [304]: result
Out[304]:
one two three four key
0 0.467976 -0.038649 -0.295344 -1.824726 L
1 -0.358893 1.404453 0.704965 -0.200638 B
2 -0.501840 0.659254 -0.421691 -0.057688 G
3 0.204886 1.074134 1.388361 -0.982404 R
4 0.354628 -0.133116 0.283763 -0.837063 Q
In [305]: chunker = pd.read_csv('../source/ch06/ex6.csv',chunksize=1000)
In [306]: chunker
Out[306]: <pandas.io.parsers.TextFileReader at 0x1147e5850>
1.2 将数据写到文本格式
In [323]: data = pd.read_csv('ex5.csv')
In [324]: data
Out[324]:
something a b c d message
0 one 1 2 3.0 4 NaN
1 two 5 6 NaN 8 world
2 three 9 10 11.0 12 foo
In [325]: data.to_csv('out.csv')
In [326]: cat out.csv
,something,a,b,c,d,message
0,one,1,2,3.0,4,
1,two,5,6,,8,world
2,three,9,10,11.0,12,foo
In [327]: data.to_csv('out.csv',sep="|")
In [328]: cat out.csv
|something|a|b|c|d|message
0|one|1|2|3.0|4|
1|two|5|6||8|world
2|three|9|10|11.0|12|foo
In [329]: import sys
In [330]: data.to_csv(sys.stdout,na_rep='NULL')
,something,a,b,c,d,message
0,one,1,2,3.0,4,NULL
1,two,5,6,NULL,8,world
2,three,9,10,11.0,12,foo
In [331]: data.to_csv(sys.stdout,index=False,header=False)
one,1,2,3.0,4,
two,5,6,,8,world
three,9,10,11.0,12,foo
In [332]: data.to_csv(sys.stdout,index=False,columns=list('abc'))
a,b,c
1,2,3.0
5,6,
9,10,11.0
Series也有类似方法
In [333]: dates = pd.date_range('2/1/2017',periods=7)
In [334]: s1 = Series(np.arange(7),index=dates)
In [335]: s1.to_csv(sys.stdout)
2017-02-01,0
2017-02-02,1
2017-02-03,2
2017-02-04,3
2017-02-05,4
2017-02-06,5
2017-02-07,6
1.3 手工处理分隔符
CSV文件的形式有很多,只需要定义csv.Dialect的一个子类接口。

In [340]: import csv
In [341]: class my_dialect(csv.Dialect):
...: lineterminator = "\n"
...: delimiter = ";"
...:
...:
In [342]: with open("mydata.csv",'w') as f:
...: writer = csv.writer(f,dialect = my_dialect)
...: writer.writerow(('one','two','three'))
...: writer.writerow(('1','2','3'))
1.4 JSON数据
JSON数据格式十分灵活
- 键都是字符串类型
- 使用python标准库json
In [344]: import json
In [350]: obj = {'name':'alex','age':18,'job':'enginer'}
In [353]: a = json.dumps(obj)
In [354]: a
Out[354]: '{"job": "enginer", "age": 18, "name": "alex"}'
In [355]: json.loads(a)
Out[355]: {u'age': 18, u'job': u'enginer', u'name': u'alex'}
1.5 xml和html:web信息收集
lxml是python处理xml的库。
- lxml.html
- lxml.objectify
待续。。
2 二进制数据格式
实现二进制数据存储最方便的方式就是使用python标准库pickle序列化。
In [356]: frame = pd.read_csv('ex1.csv')
In [357]: frame
Out[357]:
a b c d message
0 1 2 3 4 hello
1 5 6 7 8 world
2 9 10 11 12 foo
In [358]: frame.save('frame_pickle') # 没这个方法了。
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
AttributeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-358-f936768749d3> in <module>()
----> 1 frame.save('frame_pickle')
/Users/yangfeilong/anaconda/lib/python2.7/site-packages/pandas/core/generic.pyc in __getattr__(self, name)
2670 if name in self._info_axis:
2671 return self[name]
-> 2672 return object.__getattribute__(self, name)
2673
2674 def __setattr__(self, name, value):
AttributeError: 'DataFrame' object has no attribute 'save'
2.1 使用HDF5格式
HDF5流行的工业库,支持多种压缩器的即时压缩,更有效的存储数据。对于那些很大,但是不能存放在内存中的数据, hdf5是一个不错的选择。
python有两个库处理HDF5接口:
- PyTables
- h5py
pandas有一个HDFStore的类,它通过PyTables存储pandas对象。
In [359]: store = pd.HDFStore('myhdf.h5')
In [360]: frame
Out[360]:
a b c d message
0 1 2 3 4 hello
1 5 6 7 8 world
2 9 10 11 12 foo
In [361]: store['obj1'] = frame
In [362]: store['obj1_col'] = frame['a']
In [363]: store
Out[363]:
<class 'pandas.io.pytables.HDFStore'>
File path: myhdf.h5
/obj1 frame (shape->[3,5])
/obj1_col series (shape->[3])
In [367]: store['obj1']
Out[367]:
a b c d message
0 1 2 3 4 hello
1 5 6 7 8 world
2 9 10 11 12 foo
2.2 读取ms excel文件
In [368]: xls = pd.ExcelFile('data.xls')
In [369]: table = xls.parse('Sheet1')
3 使用html和web api
使用request库可以很容易的处理web api,简单的get一个url:
In [373]: import requests
In [374]: url = "http://www.baidu.com"
In [375]: resp = requests.get(url)
In [376]: resp
Out[376]: <Response [200]>
4 使用数据库
4.1 sqlite存取数据
In [388]: import sqlite3
In [390]: con = sqlite3.connect(':memory:')
In [394]: query = '''
...: CREATE TABLE test
...: (a VARCHAR(20),
...: b VARCHAR(20),
...: c REAL,
...: d INTEGER);'''
In [395]: con.execute(query)
Out[395]: <sqlite3.Cursor at 0x117414dc0>
In [396]: con.commit()
In [399]: data = [('hello','123',1.25,6),('world','Beijing',2.0,3),('foo','shanghai',2.1,20)]
In [400]: data
Out[400]:
[('hello', '123', 1.25, 6),
('world', 'Beijing', 2.0, 3),
('foo', 'shanghai', 2.1, 20)]
In [401]: stmt = "INSERT INTO test VALUES(?,?,?,?)"
In [403]: con.executemany(stmt,data)
Out[403]: <sqlite3.Cursor at 0x1174148f0>
In [404]: con.commit()
In [405]: cursor = con.execute('select * from test;')
In [406]: cursor
Out[406]: <sqlite3.Cursor at 0x1174145e0>
In [407]: cursor.fetchall()
Out[407]:
[(u'hello', u'123', 1.25, 6),
(u'world', u'Beijing', 2.0, 3),
(u'foo', u'shanghai', 2.1, 20)]
In [419]: cursor = con.execute('select * from test')
In [420]: df = cursor.fetchall()
In [421]: df
Out[421]:
[(u'hello', u'123', 1.25, 6),
(u'world', u'Beijing', 2.0, 3),
(u'foo', u'shanghai', 2.1, 20)]
In [422]: DataFrame(df,columns=zip(*cursor.description)[0])
Out[422]:
a b c d
0 hello 123 1.25 6
1 world Beijing 2.00 3
2 foo shanghai 2.10 20
同样DataFrame也可以:
In [423]: import pandas.io.sql as sql
In [425]: sql.read_sql('select * from test',con)
Out[425]:
a b c d
0 hello 123 1.25 6
1 world Beijing 2.00 3
2 foo shanghai 2.10 20
4.2 存取mongodb数据
待续。。。